先看OC关于NSObject的源码
一、alloc与init
NSObject *obj = [NSObject alloc]init];
alloc与init发生了什么呢?
+ (id)alloc {
return _objc_rootAlloc(self);
}
id _objc_rootAlloc(Class cls)
{
#if 0 && __OBJC2__
// Skip over the +allocWithZone: call if the class doesn't override it.
// fixme not - this breaks ObjectAlloc
if (! ((class_t *)cls)->isa->hasCustomAWZ()) {
return class_createInstance(cls, 0);
}
#endif
return [cls allocWithZone: nil];
}
id class_createInstance(Class cls, size_t extraBytes) {
return _class_createInstanceFromZone(cls, extraBytes, nil);
}
static id _class_createInstanceFromZone(Class cls, size_t extraBytes, void *zone, bool cxxConstruct = true, size_t *outAllocatedSize = nil) {
size_t size = cls->instanceSize(extraBytes);
id obj = (id)calloc(1, size);
if (!obj) return nil;
obj->initInstanceIsa(cls, hasCxxDtor);
return obj;
}
可以看出,alloc类方法是开辟了一块内存,生成了一个实例对象,并且对实例对象进行了初始化
- (id)init {
return _objc_rootInit(self);
}
id _objc_rootInit(id obj)
{
// In practice, it will be hard to rely on this function.
// Many classes do not properly chain -init calls.
return obj;
}
init方法只是返回了该实例对象
二、NSObject与Class
1、对象
NSObject
@interface NSObject <NSObject>
{
Class isa;
}
@end
每一个NSObject里都有一个Class(isa指针),表明这个类的类别Class
id类型
typedef struct objc_object {
Class isa;
} *id;
从上面可以看出id类型里面也有一个Class
2、Class
Class的定义
typedef struct objc_class *Class;
objc_class
struct objc_class {
Class isa;
#if !__OBJC2__
Class super_class OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
const char *name OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
long version OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
long info OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
long instance_size OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
struct objc_ivar_list *ivars OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
struct objc_method_list **methodLists OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
struct objc_cache *cache OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
struct objc_protocol_list *protocols OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
#endif
} OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
isa指针指向哪里?

从图上的虚线箭头就能看出,实例对象的isa指向类,类的isa指向元类(meta),元类的isa指向Root元类
三、isKindOfClass与isMemberOfClass
1、获取class
+ (Class)class {
return self;
}
- (Class)class {
return object_getClass(self);
}
static inline Class _object_getClass(id obj)
{
#if SUPPORT_TAGGED_POINTERS
if (OBJC_IS_TAGGED_PTR(obj)) {
uint8_t slotNumber = ((uint8_t) (uint64_t) obj) & 0x0F;
Class isa = _objc_tagged_isa_table[slotNumber];
return isa;
}
#endif
if (obj) return obj->isa;
else return Nil;
}
从上面可以看到,class类方法和实例方法都是获取当前Class也就是isa指针
- 实例方法调用时,通过对象的 isa 在类中获取方法的实现
- 类方法调用时,通过类的 isa 在元类中获取方法的实现
2、isMemberOfClass
isMemberOfClass: Returns a Boolean value that indicates whether the receiver is an instance of a given class.
+ (BOOL)isMemberOfClass:(Class)cls {
return object_getClass((id)self) == cls;
}
- (BOOL)isMemberOfClass:(Class)cls {
return [self class] == cls;
}
可以看出,isMemberOfClass是判断当前实例/类是否是那个类型
3、isKindOfClass
isKindOfClass: Returns a Boolean value that indicates whether the receiver is an instance of given class or an instance of any class that inherits from that class.
+ (BOOL)isKindOfClass:(Class)cls {
for (Class tcls = object_getClass((id)self); tcls; tcls = class_getSuperclass(tcls)) {
if (tcls == cls) return YES;
}
return NO;
}
- (BOOL)isKindOfClass:(Class)cls {
for (Class tcls = [self class]; tcls; tcls = class_getSuperclass(tcls)) {
if (tcls == cls) return YES;
}
return NO;
}
isKindOfClass是用来判断实例/类是否是那个类型,或者继承自那个类。
经典题目
BOOL res1 = [(id)[NSObject class] isKindOfClass:[NSObject class]]; //YES
BOOL res2 = [(id)[NSObject class] isMemberOfClass:[NSObject class]]; //NO
BOOL res3 = [(id)[Sark class] isKindOfClass:[Sark class]]; //NO
BOOL res4 = [(id)[Sark class] isMemberOfClass:[Sark class]]; //NO
NSObject = [NSObject class]
[NSObject isMemberOfClass:NSObject]?
题目变成:
object_getClass(NSObject)==NSObject?
metat_NSObject = object_getClass(NSObject)
所以最终题目转化为
metat_NSObject != NSObject? ==> NO;
四、KVO与KVC
1、KVO(Key-Value Observing)
先看看官方文档
Key-Value Observing Implementation Details Automatic key-value observing is implemented using a technique called isa-swizzling. The isa pointer, as the name suggests, points to the object’s class which maintains a dispatch table. This dispatch table essentially contains pointers to the methods the class implements, among other data. When an observer is registered for an attribute of an object the isa pointer of the observed object is modified, pointing to an intermediate class rather than at the true class. As a result the value of the isa pointer does not necessarily reflect the actual class of the instance. You should never rely on the isa pointer to determine class membership. Instead, you should use the class method to determine the class of an object instance.
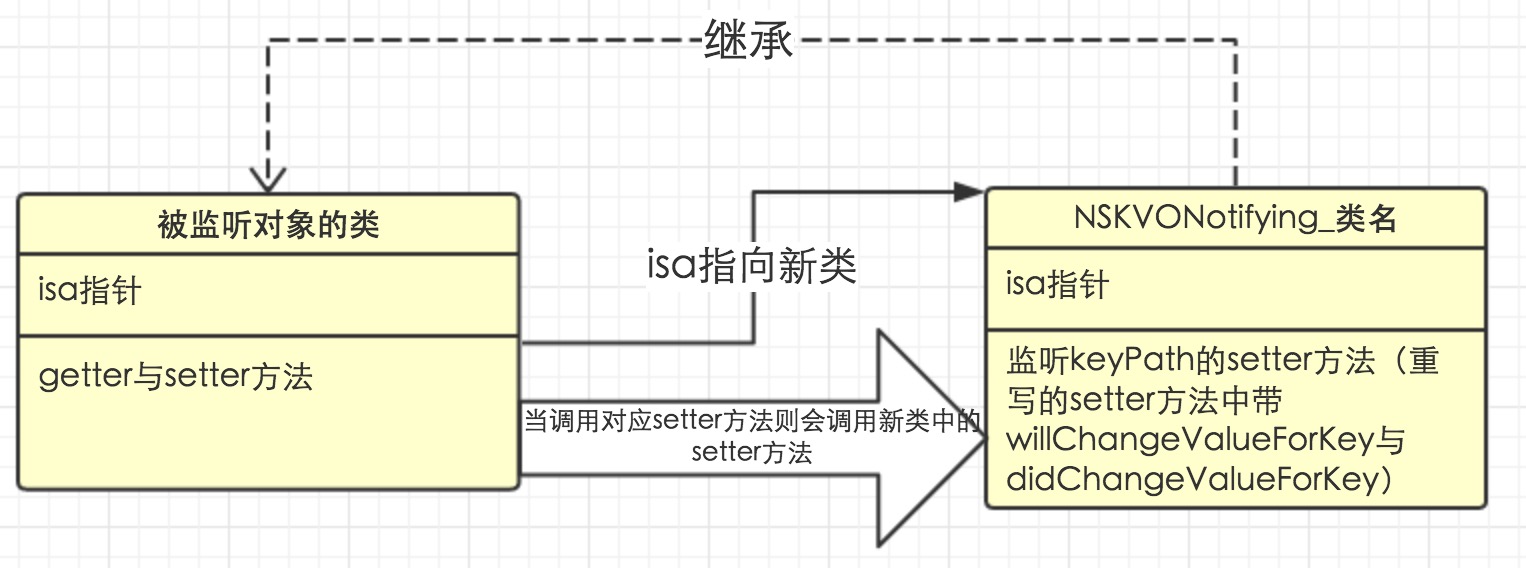
KVO运用了一个isa-swizzling的机制,runtime还有一个method-swizzling的机制,称为’黑魔法’。
当某个类的对象第一次被观察时,系统就会在运行期动态地创建该类的一个派生类,在这个派生类中重写基类中任何被观察属性的 setter 方法。然后在派生类的setter方法里实现通知机制。
同时派生类还重写了 class 方法以“欺骗”外部调用者它就是起初的那个类。然后系统将这个对象的 isa 指针指向这个新诞生的派生类,因此这个对象就成为该派生类的对象了,因而在该对象上对 setter 的调用就会调用重写的 setter,从而激活键值通知机制。此外,派生类还重写了 dealloc 方法来释放资源。
当没有observer观察任何一个property时,删除动态创建的子类。
简单而言:实例对象在被观察时,生成派生类,派生类在setter方法中valuewillchange方法和valuesdidchanged方法里发出通知,并且通过isa-swizzling,从而使实例对象成为派生类的对象,所以实例对象在setter属性时可以产生通知。达到观察的目的。
2、KVC(Key Value Coding)
KVC是是一种可以通过字符串的名字(key)来访问类属性的机制。
修改值 setValue:forKey: setValue:forKeyPath: setValue:forUnderfinedKey: setNilValueForKey: 对非类对象属性设置nil时调用,默认抛出异常。
1、首先搜索setKey:方法。(key指成员变量名,首字母大写)
2、上面的setter方法没找到,如果类方法accessInstanceVariablesDirectly返回YES。那么按 _key,_isKey,key,iskey的顺序搜索成员名。(NSKeyValueCodingCatogery中实现的类方法,默认实现为返回YES)
3、如果没有找到成员变量,调用setValue:forUnderfinedKey:
获取值 valueForKey: 传入NSString属性的名字。 valueForKeyPath: 属性的路径,xx.xx valueForUndefinedKey 默认实现是抛出异常,可重写这个函数做错误处理
1、首先按getKey,key,isKey的顺序查找getter方法,找到直接调用。如果是BOOL、int等内建值类型,会做NSNumber的转换。
2、上面的getter没找到,查找countOfKey、objectInKeyAtindex、KeyAtindexes格式的方法。如果countOfKey和另外两个方法中的一个找到,那么就会返回一个可以响应NSArray所有方法的代理集合的NSArray消息方法。
3、还没找到,查找countOfKey、enumeratorOfKey、memberOfKey格式的方法。如果这三个方法都找到,那么就返回一个可以响应NSSet所有方法的代理集合。 4、还是没找到,如果类方法accessInstanceVariablesDirectly返回YES。那么按 _key,_isKey,key,iskey的顺序搜索成员名。
5、再没找到,调用valueForUndefinedKey。
原理
isa指针(is kind of 的意思)指向维护分发表的对象的类,该分发表实际上包含了指向实现类中的方法的指针和其他数据。比如说如下的一行KVC代码:
[site setValue:@"sitename" forKey:@"name"];
//会被编译器处理成
SEL sel = sel_get_uid(setValue:forKey);
IMP method = objc_msg_loopup(site->isa,sel);
method(site,sel,@"sitename",@"name");
每个类都有一张方法表,是一个hash表,值是还书指针IMP,SEL的名称就是查表时所用的键。
SEL数据类型:查找方法表时所用的键。定义成char*,实质上可以理解成int值。
IMP数据类型:他其实就是一个编译器内部实现时候的函数指针。当Objective-C编译器去处理实现一个方法的时候,就会指向一个IMP对象,这个对象是C语言表述的类型。
五、Self与Super
1、[self class]与[super class]
有一个有意思的题目,有一个Son类继承自Father类
@implementation Son : Father
- (id)init
{
self = [super init];
if (self) {
NSLog(@"%@", NSStringFromClass([self class]));
NSLog(@"%@", NSStringFromClass([super class]));
}
return self;
}
@end
最终结果都是Son,为什么呢?
官方文档中self相关解释 Whenever you’re writing a method implementation, you have access to an important hidden value, self. Conceptually, self is a way to refer to “the object that’s received this message.” It’s apointer, just like the greeting value above, and can be used to call a method on the current receiving object. super解释 There’s anotherimportant keyword available to you in Objective-C, called super. Sending a message to super is a way to call through to a method implementation defined by a superclass further up the inheritance chain. The most common use of super is when overriding a method.
简而言之是self调用自己方法,super调用父类方法
但是底层原理呢?我们知道,OC的消息转发机制,当self时,方法转换成
id objc_msgSend(id receiver, SEL theSelector, ...)
objc_msgSend sends a message with a simple return value to an instance of a class
而super关键字调用方法则转换成
id objc_msgSendSuper(struct objc_super *super, SEL op, ...)
struct objc_super {
id receiver;
Class superClass;
};
objc_msgSendSuper sends a message with a simple return value to the superclass of an instance of a class.
可以看到objc_msgSendSuper的receiver还是son。
objc_msgSend与objc_msgSendSuperd都去查找class的Seletor,一直查到NSObject类才查到class方法
- (Class)class {
return object_getClass(self);
}
也就是说,最终都是调用的receiver也就是son,获取到了Class.
2、self = [super init]
If a class does implement an initializer, it should invoke an initializer of its superclass as the first step. This requirement ensures a series of initializations for an object down the inheritance chain, starting with the root object. The
NSObjectclass declares theinitmethod as the default object initializer, so it is always invoked last but returns first.
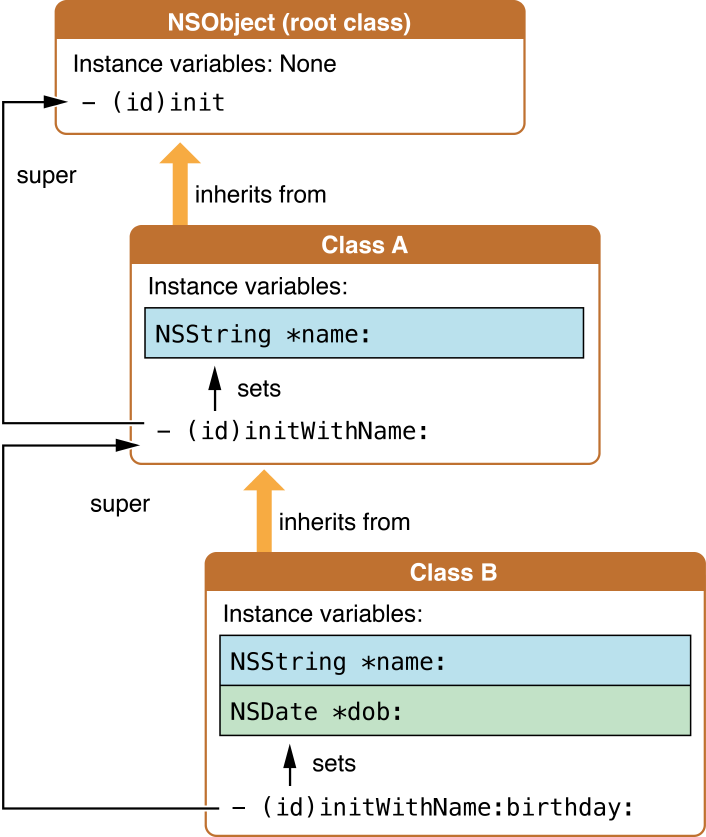
所以标准的初始化代码
- (id)init {
if (self = [super init]) { // equivalent to "self does not equal nil"
self ...
}
return self;
}
六、属性与变量(property & instance variable)
在ios5以后我们使用@property来声明属性变量,编译器会自动(@syntheszie var = _var)为我们生成对应的一个以下 划线加属性名 命名的实例变量,还有其对应的getter、setter
@property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *var;
------------------等效分割线------------------
NSString *_var;
- (NSString *)var {
return _var;
}
- (void)setVar:(NSString *)var {
_var = var;
}
这样一来我们就可以看出通过self.var和_var访问实例变量的区别,在.m文件中可以通过_var来访问实例变量,但是getter、setter不会被调用,而来自外部的访问,需要通过getter、setter。
注意,使用readonly关键字修饰后,编译器只会为我们生成getter。
假如一个属性被关键字@dynamic所修饰,则编译器不会自动生成其对应的getter、setter,然而如果开发者没有自行创造getter、setter,将不会在编译期提醒,运行时触发则会发生crash。 顺便一提@dynamic还能帮助我们替换掉某类中本来就存在的,而我们又想自己创造的property。