一、事件
iOS里有三种事件:触摸(touch)、加速(motion)、远程控制
在UIResponder里,有以下事件处理
// 触摸事件
- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event;
- (void)touchesMoved:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event;
- (void)touchesEnded:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event;
- (void)touchesCancelled:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event;
// 加速计事件
- (void)motionBegan:(UIEventSubtype)motion withEvent:(UIEvent *)event;
- (void)motionEnded:(UIEventSubtype)motion withEvent:(UIEvent *)event;
- (void)motionCancelled:(UIEventSubtype)motion withEvent:(UIEvent *)event;
// 远程控制事件
- (void)remoteControlReceivedWithEvent:(UIEvent *)event;
二、寻找响应者(UIResponder)-事件传递
响应者:继承UIResponder的对象称之为响应者对象,能够处理touchesBegan等触摸事件
当一个Touch事件产生时,要先找到响应者,iOS通过Hit-Test机制来寻找响应者,每一个UIView(继承自UIResponder)都有以下的方法
- (nullable UIView *)hitTest:(CGPoint)point withEvent:(nullable UIEvent *)event;
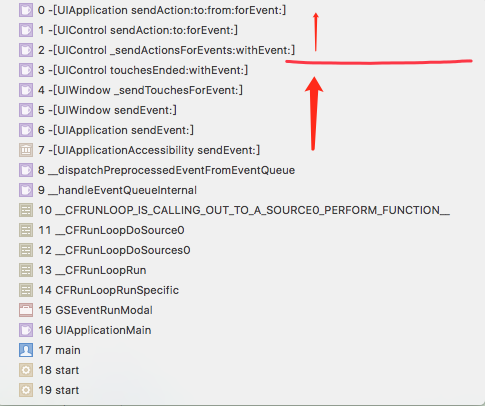
HitTest的顺序
UIApplication -> UIWindow -> Root View -> subview -> ··· -> initalView
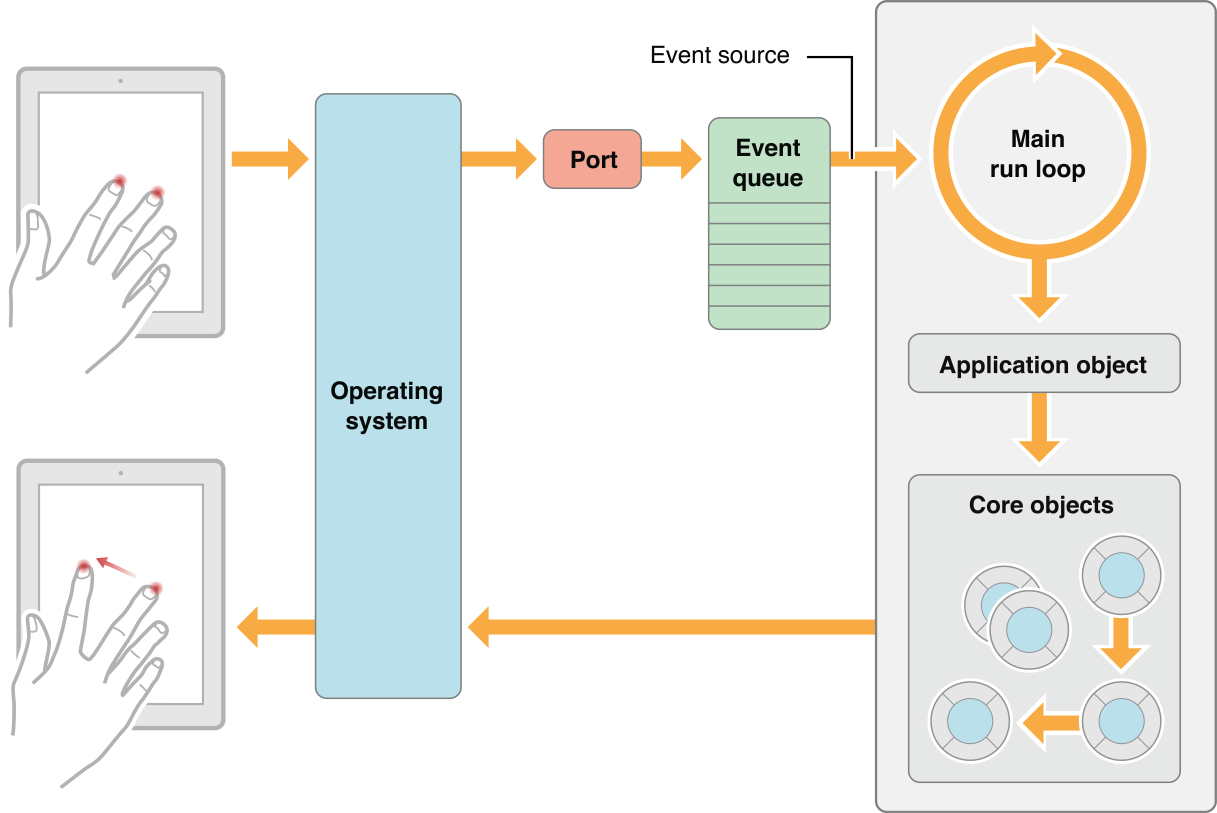
- 系统检测到手指触摸(Touch)操作时,将Touch 以UIEvent的方式加入UIApplication事件队列中。
- UIApplication从事件队列中取出最新的触摸事件进行分发传递到UIWindow进行处理。
- UIApplication和UIWindow通过
sendEvent:方法传递事件 - UIWindow 之后会通过
hitTest:withEvent:方法寻找触碰点所在的视图
hitTest:withEvent:原理
// point是该视图的坐标系上的点
- (UIView *)hitTest:(CGPoint)point withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
// 1.判断自己能否接收触摸事件
if (self.userInteractionEnabled == NO || self.hidden == YES || self.alpha <= 0.01) return nil;
// 2.判断触摸点在不在自己范围内
if (![self pointInside:point withEvent:event]) return nil;
// 3.从后往前遍历自己的子控件,看是否有子控件更适合响应此事件
int count = self.subviews.count;
for (int i = count - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
UIView *childView = self.subviews[i];
CGPoint childPoint = [self convertPoint:point toView:childView];
UIView *fitView = [childView hitTest:childPoint withEvent:event];
if (fitView) {
return fitView;
}
}
// 没有找到比自己更合适的view
return self;
}
三、响应者链条
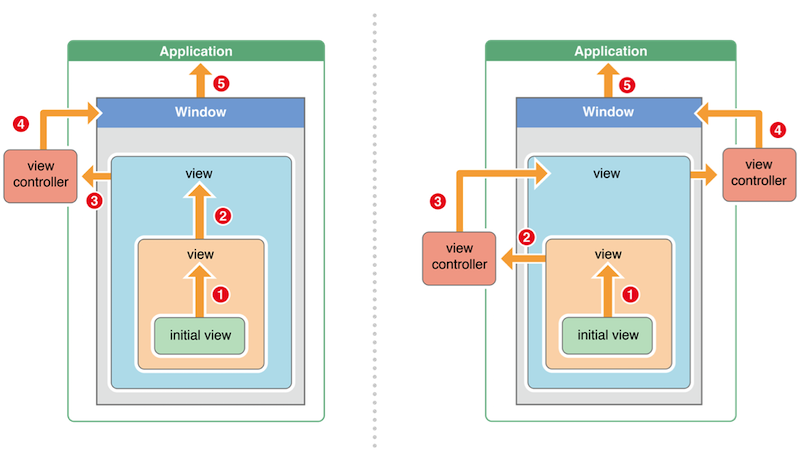
当找到最合适的响应者之后, 便会调用控件相应的touches方法来作具体处理. 并将该事件随着响应者链条往回传递, 交给上一个响应者来处理. (即调用super的touches方法),从之前往下走的路线往上回传,在其中加入了Viewtroller来处理
-
如果view的控制器存在,就传递给控制器;如果控制器不存在,则将其传递给它的父View
-
在视图层次结构的最顶级视图,传递给ViewController
-
ViewController将事件传递给window对象进行处理
-
window对象继续将事件或消息传递给UIApplication对象
-
如果UIApplication也不能处理该事件或消息,响应者链条从头到尾,都未处理,则将其丢弃
事件不处理,指的是
touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event;方法不写。
四、实例分析
UIButton的继承链是:
UIButton->UIControl->UIView->UIResponder->NSObject
UIApplication能够接受事件,因为UIApplication和UIView一样继承自UIResponder
下面是一个点击事件的方法过程
UIButton *button = [UIButton buttonWithType:UIButtonTypeContactAdd];
button.frame = CGRectMake(100, 100, 40, 40);
[button addTarget:self action:@selector(click) forControlEvents:UIControlEventTouchUpInside];
[self.view addSubview:button];