其他两篇关于Runloop:
苹果官方文档:Run loops
一、定义一个Custom Input Source
Creating a custom input source involves defining the following:
- The information you want your input source to process.
- A scheduler routine to let interested clients know how to contact your input source.
- A handler routine to perform requests sent by any clients.
- A cancellation routine to invalidate your input source.
Because you create a custom input source to process custom information, the actual configuration is designed to be flexible. The scheduler, handler, and cancellation routines are the key routines you almost always need for your custom input source. Most of the rest of the input source behavior, however, happens outside of those handler routines. For example, it is up to you to define the mechanism for passing data to your input source and for communicating the presence of your input source to other threads.
创建一个自定义的input source需要涉及以下几点:
- 需要input source处理的信息
- 调度程序让需要的端口知道怎么连接你的input source
- 可用的程序来处理任意端口发出的请求
- 有程序来取消input source
因为创建一个自定义的input source来处理自定义信息,可配置的还是很灵活的,调度程序、处理程序和取消是关键。其他的input source就是在这些程序之外。
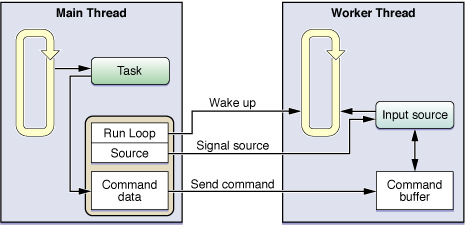
Figure shows a sample configuration of a custom input source. In this example, the application’s main thread maintains references to the input source, the custom command buffer for that input source, and the run loop on which the input source is installed. When the main thread has a task it wants to hand off to the worker thread, it posts a command to the command buffer along with any information needed by the worker thread to start the task. (Because both the main thread and the input source of the worker thread have access to the command buffer, that access must be synchronized.) Once the command is posted, the main thread signals the input source and wakes up the worker thread’s run loop. Upon receiving the wake up command, the run loop calls the handler for the input source, which processes the commands found in the command buffer
下图展示了配置一个自定义input sources,主线程操控维护了input source的引用、input source的命令缓存区、input source安装在的那个runloop。当主线程有任务想要交给工作线程去处理,主线程发送命令到command buffer命令缓存区(命令带了工作线程工作所需的)。主线程和工作线程的input source都可以访问command buffer命令缓存区,所以这个访问必须是同步的。一旦命令发出,主线程通知input source并且唤醒工作线程的runloop。runloop一旦接到唤醒命令,runloop就会回调处理方法给input source,处理在command buffer命令缓存区里找到的命令。
@interface RunLoopSource : NSObject
{
CFRunLoopSourceRef runLoopSource;
NSMutableArray* commands;
}
- (id)init;
- (void)addToCurrentRunLoop;
- (void)invalidate;
// Handler method
- (void)sourceFired;
// Client interface for registering commands to process
- (void)addCommand:(NSInteger)command withData:(id)data;
- (void)fireAllCommandsOnRunLoop:(CFRunLoopRef)runloop;
@end
The
RunLoopSourceobject manages a command buffer and uses that buffer to receive messages from other threads
RunLoopSource对象管理了一个command buffer并且用buffer来从其他线程接受信息。
// These are the CFRunLoopSourceRef callback functions.
void RunLoopSourceScheduleRoutine (void *info, CFRunLoopRef rl, CFStringRef mode);
void RunLoopSourcePerformRoutine (void *info);
void RunLoopSourceCancelRoutine (void *info, CFRunLoopRef rl, CFStringRef mode);
// RunLoopContext is a container object used during registration of the input source.
@interface RunLoopContext : NSObject
{
CFRunLoopRef runLoop;
RunLoopSource* source;
}
@property (readonly) CFRunLoopRef runLoop;
@property (readonly) RunLoopSource* source;
- (id)initWithSource:(RunLoopSource*)src andLoop:(CFRunLoopRef)loop;
@end
RunLoopContextobject, which is really just a container object used to pass aRunLoopSourceobject and a run loop reference to the application’s main thread.
RunLoopContext对象是一个容器,用来传递RunLoopSource对象和runloop引用给主线程。
The first of these functions is called when you actually attach the run loop source to your run loop,Because this input source has only one client (the main thread), it uses the scheduler function to send a message to register itself with the application delegate on that thread. When the delegate wants to communicate with the input source, it uses the information in
RunLoopContextobject to do so
当你把runloop source放入到runloop时,实际会调用下面这个函数。因为input source只有一个端口(主线程),input source使用调度函数来发送一个消息从而注册他本身到线程的delegate上,当delegate用RunLoopContext与input source交流,
void RunLoopSourceScheduleRoutine (void *info, CFRunLoopRef rl, CFStringRef mode)
{
RunLoopSource* obj = (RunLoopSource*)info;
AppDelegate* del = [AppDelegate sharedAppDelegate];
RunLoopContext* theContext = [[RunLoopContext alloc] initWithSource:obj andLoop:rl];
[del performSelectorOnMainThread:@selector(registerSource:)
withObject:theContext waitUntilDone:NO];
}
One of the most important callback routines is the one used to process custom data when your input source is signaled. Listing 3-5 shows the perform callback routine associated with the
RunLoopSourceobject. This function simply forwards the request to do the work to thesourceFiredmethod, which then processes any commands present in the command buffer.
最重要之一的回调是当input sour发完信号时处理自定义的数据,下面的代码展示了RunLoopSource的处理回调。这个函数简单地将需求转发到sourceFired方法(处理任何在命令缓存池的命令)
void RunLoopSourcePerformRoutine (void *info)
{
RunLoopSource* obj = (RunLoopSource*)info;
[obj sourceFired];
}
f you ever remove your input source from its run loop using the
CFRunLoopSourceInvalidatefunction, the system calls your input source’s cancellation routine. You can use this routine to notify clients that your input source is no longer valid and that they should remove any references to it
如果你使用CFRunLoopSourceInvalidate这个函数来将input source移除,系统会调input source的移除例程函数,你可以用这个例程函数来通知客户端你的input source不再可用而且应该移除相关。
void RunLoopSourceCancelRoutine (void *info, CFRunLoopRef rl, CFStringRef mode)
{
RunLoopSource* obj = (RunLoopSource*)info;
AppDelegate* del = [AppDelegate sharedAppDelegate];
RunLoopContext* theContext = [[RunLoopContext alloc] initWithSource:obj andLoop:rl];
[del performSelectorOnMainThread:@selector(removeSource:)
withObject:theContext waitUntilDone:YES];
}
将input source放入runloop
Installation of the input source does not occur until the worker thread invokes the
addToCurrentRunLoopmethod, at which point theRunLoopSourceScheduleRoutinecallback function is called. Once the input source is added to the run loop, the thread can run its run loop to wait on it.
在工作线程调用addToCurrentRunLoop方法之前,input source并不会install,这个时候会调用RunLoopSourceScheduleRoutine回调函数,一旦input source被添加进runloop,线程就开始运行runloop.
- (id)init
{
CFRunLoopSourceContext context = {0, self, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL,
&RunLoopSourceScheduleRoutine,
RunLoopSourceCancelRoutine,
RunLoopSourcePerformRoutine};
runLoopSource = CFRunLoopSourceCreate(NULL, 0, &context);
commands = [[NSMutableArray alloc] init];
return self;
}
- (void)addToCurrentRunLoop
{
CFRunLoopRef runLoop = CFRunLoopGetCurrent();
CFRunLoopAddSource(runLoop, runLoopSource, kCFRunLoopDefaultMode);
}
调度input source的客户端
For your input source to be useful, you need to manipulate it and signal it from another thread. The whole point of an input source is to put its associated thread to sleep until there is something to do. That fact necessitates having other threads in your application know about the input source and have a way to communicate with it.
One way to notify clients about your input source is to send out registration requests when your input source is first installed on its run loop. You can register your input source with as many clients as you want, or you can simply register it with some central agency that then vends your input source to interested clients.
Listing 3-8 shows the registration method defined by the application delegate and invoked when the
RunLoopSourceobject’s scheduler function is called. This method receives theRunLoopContextobject provided by theRunLoopSourceobject and adds it to its list of sources. This listing also shows the routine used to unregister the input source when it is removed from its run loop.
为了使input source变得有用,需要操纵input source并从其他线程发出信号。输入源的全部要点是将线程休眠直到有事情做,这样的话就需要线程知道Input souce并与之沟通.
告诉客户端关于input source的一种方法就是当input source第一次installed在runloop时放一个注册需求。你可以注册随意多的客户端,或者简单地注册到一个中央机构可以将input source转交给客户端。
下面的代码显示了当调用RunloopSource对象的调度程序函数时,由程序delegate定义并调用的注册方法。这个方法接受RunLoopSource对象提供的RunLoopContext对象并将其添加到源列表里。代码还显示了当从runloop里移除input source时将其注销
- (void)registerSource:(RunLoopContext*)sourceInfo;
{
[sourcesToPing addObject:sourceInfo];
}
- (void)removeSource:(RunLoopContext*)sourceInfo
{
id objToRemove = nil;
for (RunLoopContext* context in sourcesToPing)
{
if ([context isEqual:sourceInfo])
{
objToRemove = context;
break;
}
}
if (objToRemove)
[sourcesToPing removeObject:objToRemove];
}
给input source发出信号
After it hands off its data to the input source, a client must signal the source and wake up its run loop. Signaling the source lets the run loop know that the source is ready to be processed. And because the thread might be asleep when the signal occurs, you should always wake up the run loop explicitly. Failing to do so might result in a delay in processing the input source.
Listing 3-9 shows the
fireCommandsOnRunLoopmethod of theRunLoopSourceobject. Clients invoke this method when they are ready for the source to process the commands they added to the buffer
在将数据交给input soure之后,客户端必须向souce发出信号并将runloop唤醒。向source发出信号让runloop知道source已可以被处理,并且因为线程有可能已经休眠,所以当信号发出的时候,你必须明确地唤醒runloop,否则会导致处理input source的延迟
下面的代码显示了RunLoopSource对象的fireCommandsOnRunLoop方法,这个方法会在当客户端准备好source来处理添加到缓存区的命令时调用。
- (void)fireCommandsOnRunLoop:(CFRunLoopRef)runloop
{
CFRunLoopSourceSignal(runLoopSource);
CFRunLoopWakeUp(runloop);
}
二、配置Timer Sources
To create a timer source, all you have to do is create a timer object and schedule it on your run loop. In Cocoa, you use the
NSTimerclass to create new timer objects, and in Core Foundation you use theCFRunLoopTimerRefopaque type. Internally, theNSTimerclass is simply an extension of Core Foundation that provides some convenience features, like the ability to create and schedule a timer using the same method.
创建一个timer source,你需要做的就是创建一个timer对象然后将其放入runloop,用NSTimer或者CFRunLoopTimerRef都可以。可以用下面的方法
scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:target:selector:userInfo:repeats:
scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:invocation:repeats:
These methods create the timer and add it to the current thread’s run loop in the default mode (
NSDefaultRunLoopMode). You can also schedule a timer manually if you want by creating yourNSTimerobject and then adding it to the run loop using theaddTimer:forMode:method ofNSRunLoop. Both techniques do basically the same thing but give you different levels of control over the timer’s configuration. For example, if you create the timer and add it to the run loop manually, you can do so using a mode other than the default mode. Listing 3-10 shows how to create timers using both techniques. The first timer has an initial delay of 1 second but then fires regularly every 0.1 seconds after that. The second timer begins firing after an initial 0.2 second delay and then fires every 0.2 seconds after that.
上面的两个方法创建一个timer并且将它以默认模式NSDefaultRunLoopMode添加到当前线程的runloop。当然你也可以手动创建一个并用addTimer:forMode:添加进runloop.两种方法都是一样的,其中一个可以配置更多。下面的方法显示了两种方法的详细
NSRunLoop* myRunLoop = [NSRunLoop currentRunLoop];
// Create and schedule the first timer.
NSDate* futureDate = [NSDate dateWithTimeIntervalSinceNow:1.0];
NSTimer* myTimer = [[NSTimer alloc] initWithFireDate:futureDate
interval:0.1
target:self
selector:@selector(myDoFireTimer1:)
userInfo:nil
repeats:YES];
[myRunLoop addTimer:myTimer forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode];
// Create and schedule the second timer.
[NSTimer scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:0.2
target:self
selector:@selector(myDoFireTimer2:)
userInfo:nil
repeats:YES];
下面这个是用Core Foundation来添加一个timer
CFRunLoopRef runLoop = CFRunLoopGetCurrent();
CFRunLoopTimerContext context = {0, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL};
CFRunLoopTimerRef timer = CFRunLoopTimerCreate(kCFAllocatorDefault, 0.1, 0.3, 0, 0,
&myCFTimerCallback, &context);
CFRunLoopAddTimer(runLoop, timer, kCFRunLoopCommonModes);
三、配置一个Port-Based Input Source
配置一个NSMachPort对象
To establish a local connection with an
NSMachPortobject, you create the port object and add it to your primary thread’s run loop. When launching your secondary thread, you pass the same object to your thread’s entry-point function. The secondary thread can use the same object to send messages back to your primary thread.
要建立一个与NSMachPort对象的本地连接,你需要创建一个port对象然后将它添加到你的主要线程的runloop.当启动辅助线程时,将相同的对象传递给线程的entry-point函数。辅助线程可以使用相同的对象将消息返回主要线程
下面代码显示了一个主要线程来启动一个辅助线程
- (void)launchThread
{
NSPort* myPort = [NSMachPort port];
if (myPort)
{
// This class handles incoming port messages.
[myPort setDelegate:self];
// Install the port as an input source on the current run loop.
[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addPort:myPort forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode];
// Detach the thread. Let the worker release the port.
[NSThread detachNewThreadSelector:@selector(LaunchThreadWithPort:)
toTarget:[MyWorkerClass class] withObject:myPort];
}
}